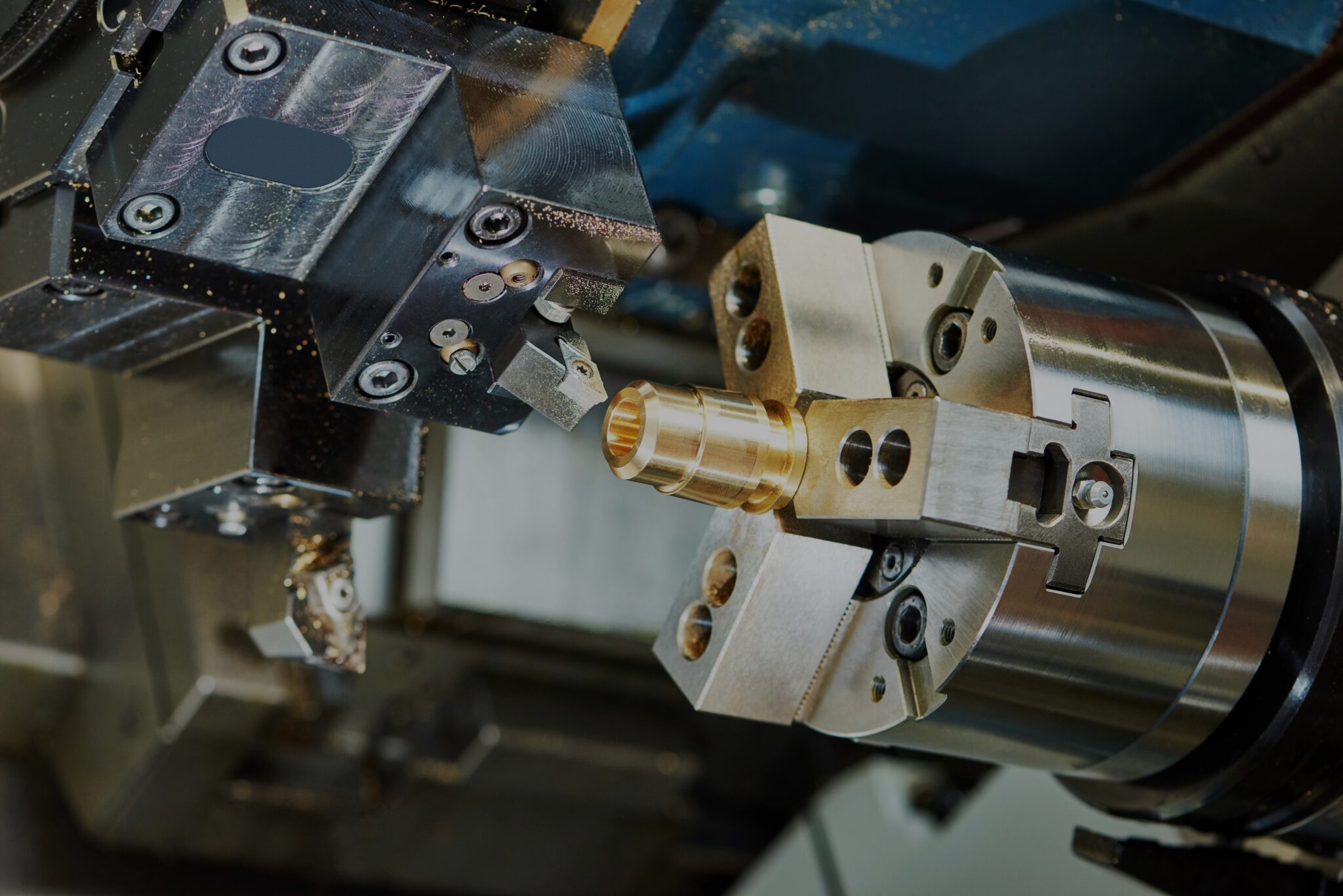
Zinc is a versatile and widely used metal in part manufacturing. It is nonmagnetic, nontoxic with good corrosion resistance properties. With the advent of CNC technology, many seek to leverage zinc’s benefits in high-precision applications. However, a common question that comes to mind is if zinc can be machined effectively.
The answer to this question is YES. It is possible to cut and shape zinc metal to produce high-quality parts. This article will be your guide on everything about CNC machining zinc. It will explain the properties of zinc that make it suitable for CNC machining, common zinc alloys you can use, and tips to get the best result.
What is CNC Machining Zinc
CNC machining zinc is the process of using Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology to cut and shape zinc alloys. The result is accurate and high-quality parts. The process of CNC machining zinc begins with creating a 2D or 3D model of the design. The model contains the exact specifications of the part to be manufactured. You carry out this step using CAD software including AutoCAD or SOLIDWORKS.
Thereafter, you convert the model to a language the machine understands in the form of G-code and M-code. G-code controls the motion and positioning of the cutting tools. It tells the machine how and where to move to perform operations including milling, turning, and drilling. On the other hand, M-code is in charge of miscellaneous functions such as tool changes, coolant control, and start or stop action.
After generating the CNC code, you set up the machine and execute the operation. As the cutting tool moves along various axes, it removes excess material from the workpiece to create the desired shape. Once the program ends, remove the part and inspect for quality.
Properties of Zinc that Make it Suitable for CNC Machining
Zinc is an ideal material for CNC machining because of its many properties. It is malleable, cost-effective, and produces high-quality structures and components. The following are the key properties that set zinc aside in CNC machining.
-
Malleability
Zinc is a highly malleable alloy. This property emphasizes how easily you can cut and shape it without damage or fracture. Furthermore, the malleability of zinc makes it more straightforward when creating complex shapes and detailed designs on the workpiece. When CNC machining zinc, you can be sure of reduced tool wear and breakage.
-
Dimensional Stability
Zinc alloy comes with the innate ability to retain its original shape and size throughout the CNC machining process. This prevents errors and allows for precise machining. Additionally, the CNC-machined zinc components are accurate and consistent. Hence, they are useful in high-tolerance applications.
-
Good Surface Finish
Zinc alloys produce a smooth and glossy surface finish during CNC machining. They have a fine grain structure which reduces the appearance of tool marks and produces a smooth finish. Furthermore, zinc has a low friction coefficient. This property minimizes friction between the workpiece and the tool and prevents surface damage.
-
High Thermal Conductivity
Zinc has a high thermal conductivity. This alloy can efficiently transfer heat and ensure quick cooling during CNC machining. Hence, there is less incidence of thermal expansion and contraction that can compromise the workpiece’s accuracy and precision.
-
Environmentally Friendly
When it comes to environmental friendliness, zinc stands out. You can easily recycle zinc alloys without fear of property loss. Furthermore, CNC machining zinc does not give off harmful and toxic fumes during an operation. Additionally, it requires less energy to cut when compared to other metals.
Common Zinc Alloys for CNC Machining
Pure zinc is usually not used alone in CNC machining because of its softness and tendency to stick to cutting tools. Most times, what you see is a product of zinc alloyed with other metals including aluminum, copper, and magnesium. The following are the most common zinc alloys you can employ for CNC machining.
-
Zamak 3
Zamak 3 is one of the most popular zinc alloys available today. It contains an average of 96% zinc with 4% aluminum in addition to traces of other elements. Zamak 3 has excellent thermal conductivity and good dimensional stability. Additionally, it is widely accessible with a moderate strength and low cost.
Applications: Household door hardware, gear knobs, and parts of industrial machines.
-
Zamak 5
Zamak 5 is similar to Zamak 3 in terms of appearance and composition. However, this alloy contains an additional 1% copper that helps to improve strength and enhance corrosion resistance. Zamak 5 is easy to machine and performs well in demanding environments. When compared to Zamak 3, Zamak 5 is less ductile.
Applications: Engine components, household enclosures, and furniture hardware.
-
ZA 8
ZA 8 is another alloy suitable for CNC machining. Its name is derived from the 8% aluminum metal it contains. ZA 8 also has small traces of copper and magnesium. Note that this high percentage of aluminum in ZA 8 helps to improve strength and hardness while lowering density. Furthermore, ZA 8 has a high wear resistance and excellent dimensional stability.
Applications: Medical devices, car components, and machine parts.
-
EZAC
This is one of the most recently developed zinc alloys known for its exceptional strength and creep resistance. It is made up of varying percentages of zinc, aluminum, copper, magnesium, and other elements in minute amounts. EZAC has high hardness and good corrosion resistance properties. However, this alloy becomes brittle when used at lower temperatures.
Applications: Automotive gears, agricultural equipment, precision instruments, and aircraft components.
-
ZA 27
ZA 27 is a specialized zinc alloy that contains up to 27% and 2.2% aluminum and copper respectively. ZA 27 is the strongest of all zinc alloys available. It is nonsparking and comes with unmatched creep properties and thermal conductivity. Furthermore, ZA 27 has good impact and wear resistance. This property makes ZA 27 suitable for high-stress uses.
Applications: High-load gears, industrial machinery, aerospace parts, and automotive components.
-
Tombak
Tombak is an alloy with a high copper content. It is made up of 72% copper and about 5-20% zinc. Note that the hardness of this alloy increases as the percentage of zinc increases. Tombak is popular because of its electrical conductivity and ease of machinability. Additionally, this alloy is ductile and resists corrosion even in humid environments.
Applications: Decorative trims, electrical connectors and terminals, door handles, and parts of musical instruments.
-
ACuZinc
ACuZinc is a zinc alloy that has 5-6% copper and 2-3% aluminum as the major elements. The copper content in ACuZinc increases its tensile strength and hardness level. Furthermore, this alloy has good wear and corrosion-resistant properties. When compared to Zamak alloys, ACuZinc has higher creep performance which ensures durability of the CNC machined parts over time.
Applications: Electrical components, marine devices, and architectural structures.
-
ZA 22
This is a zinc-aluminum alloy suitable for use in demanding environments. It contains an average of 78% zinc, 20% aluminum, and 1% copper with traces of other elements. ZA 22 has a high strength and hardness. Furthermore, this alloy comes with good corrosion, wear, and creep resistance.
Applications: Construction equipment, automotive parts, and aircraft components
Tips for Zinc CNC Machining
Zinc CNC machining yields high-quality results provided that you follow the best strategies and practices. The following are some tips and considerations for zinc CNC machining
-
Proper Tool Selection
Choosing the right cutting tool is the first step toward a successful zinc CNC machining operation. When compared to most metals, zinc is soft and requires careful handling. Always use tools made with carbide to maintain sharp cutting edges. Additionally, you can also go for tools with specific coatings to prevent the material from sticking to the tool.
-
Material Preparation
The way you prepare the workpiece will determine the result you will get. Before any machining operation, clean off all dirt, grease, and debris that can interfere with the process. Inconsistencies can lead to unwanted reactions and uneven surface finishes. Furthermore, you should preheat the zinc workpiece if necessary to avoid it from becoming brittle.
-
Prioritize Coolants
You should also use suitable coolants and lubricants during zinc CNC machining. They help to prevent overheating and provide a smooth cutting operation. You can use either oil or water-based coolant when cutting a zinc workpiece. Water-based coolants are more common as they serve as both cooling and lubrication systems. However, you will achieve a finer surface finish with oil-based coolants.
-
Optimize Machining Parameters
To get precise products, you must optimize the different cutting parameters based on the specific zinc alloy you are working on. You have to adjust the cutting speed and feed rate. Utilizing higher or lower than required speed and feed rate will lead to surface imperfections. Furthermore, use the right depth of cut and spindle speed to ensure dimensional accuracy and avoid excessive heat generation.
-
Use Appropriate Jigs and Fixtures
You must use the correct jigs and fixtures to minimize vibrations during zinc CNC machining. Because zinc is soft and prone to deformation, avoid excessive clamping force when securing the workpiece with a fixture. Furthermore, employ proper jigs to control the movement of the tool for accurate and precise cuts.
-
Chip Management
There is a high chance of chipping when cutting zinc workpieces using CNC technology. It is important to control the amount of chips produced to ensure a smooth machining operation. To properly manage chips, consider using a chip breaker on the tool side to cut chips into smaller sizes. This will prevent long chips from clogging the tools and causing irreversible damage.
Conclusion
Zinc has a unique blend of physical, chemical, and mechanical properties that makes it a popular choice in manufacturing industries. It is soft and easy to work on. Hence, zinc is perfect for CNC machining technique. While CNC machining zinc can present certain challenges, you can follow some tips and best practices to mitigate these issues. Furthermore, to get the most out of zinc machining, you have to use the right CNC machine shop. The most ideal service provider will ensure the parts meet design specifications and tolerances.