In today’s competitive marketplace, creating products that resonate with users is no longer optional—it’s essential for survival and growth. Modern consumers demand more than just visually appealing products; they seek solutions that enhance their lives in meaningful ways. As a result, businesses are shifting from a purely aesthetic approach to one that prioritizes functionality, ease of use, and emotional connection. This evolution is guided by user-centered design (UCD), a dynamic philosophy that places the user at the heart of the product design process. Unlike traditional methods that focus on market trends or technical capabilities, UCD emphasizes understanding real-world user needs, preferences, and behaviors. By engaging users throughout the design journey, companies can craft products that are not only innovative but also genuinely effective in addressing their target audience’s challenges. Let’s delve into how UCD is redefining product development and why it stands out as a game-changing approach to creating better, more impactful products.
What Is User-Centered Design
User-centered design (UCD) is a methodology grounded in the idea that users should play a central role in the entire development cycle. It goes beyond surface-level design considerations, focusing instead on gaining a profound understanding of users who they are, what they need, and how they interact with a product. This insight is then systematically woven into every phase of the product design process, ensuring the outcome aligns closely with user expectations. Unlike traditional approaches, which often prioritize aesthetics, technical constraints, or business objectives in isolation, UCD is inherently iterative and deeply problem-solving in nature. By involving users early and frequently, designers and developers continuously test, gather feedback, and refine their solutions. This approach not only enhances functionality but fosters empathy, enabling the creation of intuitive, meaningful, and highly effective products that truly resonate with users.
Principles Driving User-Centered Design Success
The effectiveness of user-centered design lies in its guiding principles, which shape every stage of the product development journey. These principles are not static rules but rather flexible strategies that adapt to diverse projects and challenges.
- One fundamental principle is empathy. UCD requires a deep dive into users’ lives to understand their motivations, frustrations, and goals. This understanding is achieved through comprehensive research, such as interviews, focus groups, and surveys, which uncover the subtle nuances of user behavior. For instance, observing how people interact with a product in real-world settings can reveal barriers or pain points that traditional testing might overlook. Designers then use these insights to create personas—detailed profiles that represent the key segments of a product’s user base. These personas serve as reference points throughout the product design process, ensuring that every decision reflects user priorities.
- Another critical element is iteration. In UCD, design is never a one-and-done activity. Prototypes are developed, tested, and refined repeatedly, with each cycle informed by user feedback. This iterative approach reduces risks and ensures that the final product is polished and well-suited to its audience. Unlike static, linear workflows, UCD’s cyclical process keeps the focus on improvement, allowing teams to adapt quickly to changing user needs or market conditions.
- Inclusivity and accessibility also play vital roles in UCD. A user-centered approach acknowledges that products should cater to diverse audiences, including individuals with disabilities or unique requirements. Designing for inclusivity not only expands the product’s potential user base but also enhances the experience for all users. Features like customizable interfaces or alternative input methods are examples of how inclusivity translates into practical design.
The Role Of The Product Design Process In UCD
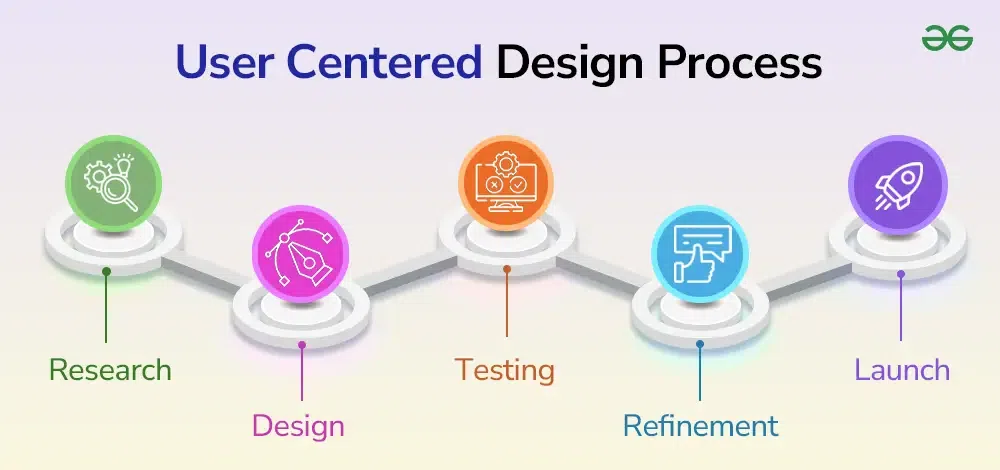
The product design process in a user-centered framework is both structured and flexible, focusing on user needs at every phase. Here’s a closer look at its key stages:
- Research and Discovery
- Every great product begins with thorough research. This phase involves gathering qualitative and quantitative data about users, their challenges, and their environment. Tools like user interviews, market analysis, and usability testing are commonly employed to identify gaps and opportunities.
- Ideation and Concept Development
- Armed with research insights, teams brainstorm potential solutions. Sketches, wireframes, and mockups take shape during this stage, each reflecting user needs and feedback. Designers use these visual aids to communicate ideas and invite input from stakeholders and users.
- Prototyping and Testing
- Prototypes bring concepts to life in a tangible form, allowing teams to test assumptions and gather user feedback. By involving users in usability tests, designers can pinpoint areas of improvement and refine the design before development begins.
- Implementation and Refinement
- During development, designers and engineers work together to bring the prototype to production. However, UCD doesn’t stop here. Post-launch feedback loops ensure the product continues to evolve and address any emerging user concerns.
- Evaluation and Feedback
- Even after a product is live, user-centered design emphasizes ongoing evaluation. Regular user surveys, analytics, and direct feedback help identify areas for updates or enhancements, keeping the product relevant and competitive.
The Tangible Benefits Of UCD
- Adopting user-centered design is not just about creating better products; it is also a sound business strategy with measurable benefits. First and foremost, UCD enhances usability. Products designed with user needs in mind are naturally more intuitive, reducing frustration and increasing satisfaction. Whether it’s a simplified app interface or a seamlessly functioning physical device, usability remains a cornerstone of successful design.
- Moreover, UCD significantly boosts engagement and retention. When users find a product easy to navigate and aligned with their expectations, they are more likely to continue using it. This creates a ripple effect, as satisfied users often become brand advocates who share their positive experiences with others.
- Another advantage of UCD is cost efficiency. Iterative testing and early user involvement prevent costly redesigns and mitigate risks during development. By addressing potential issues before a product hits the market, businesses save both time and resources. Additionally, products developed using UCD gain a competitive advantage. In a crowded marketplace, user-focused solutions stand out by delivering superior experiences that resonate on a deeper level.
Challenges And Opportunities In Adopting UCD
Despite its many advantages, implementing a user-centered design can be challenging. One of the primary hurdles is balancing business goals with user needs. While UCD emphasizes the user, companies must also meet financial objectives and timelines. This requires careful planning and clear communication among stakeholders.
Time and resource constraints can also pose challenges. Conducting extensive user research and iterative testing demands significant investment, which may be difficult for smaller teams. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial costs, making UCD a worthwhile investment.
Another challenge lies in managing diverse stakeholder expectations. Teams from different departments may have conflicting priorities, which can complicate decision-making. Building a culture of collaboration and shared understanding is essential to overcoming these barriers.
Future Of User-Centered Design
The role of UCD in the product design process is only growing as technology evolves. Emerging tools like artificial intelligence and augmented reality are transforming how designers gather insights and test solutions. AI-powered analytics, for example, provide detailed information about user behavior, enabling hyper-personalized designs. Similarly, AR technologies allow designers to simulate real-world scenarios, offering deeper insights during the development phase. Ethical design is another area where UCD is expanding. As users become more conscious of data privacy and ethical considerations, designers are incorporating transparency and trust into their products. This evolution reflects a broader trend of aligning design practices with societal values.
In conclusion, user-centered design is more than just a methodology—it is a transformative philosophy that redefines the product design process. By prioritizing users’ needs, businesses can create products that not only function effectively but also foster deep emotional connections. As industries continue to innovate, the principles of UCD will remain indispensable in shaping products that stand out in competitive markets. By embracing this approach, companies can build lasting relationships with their users and secure long-term success.