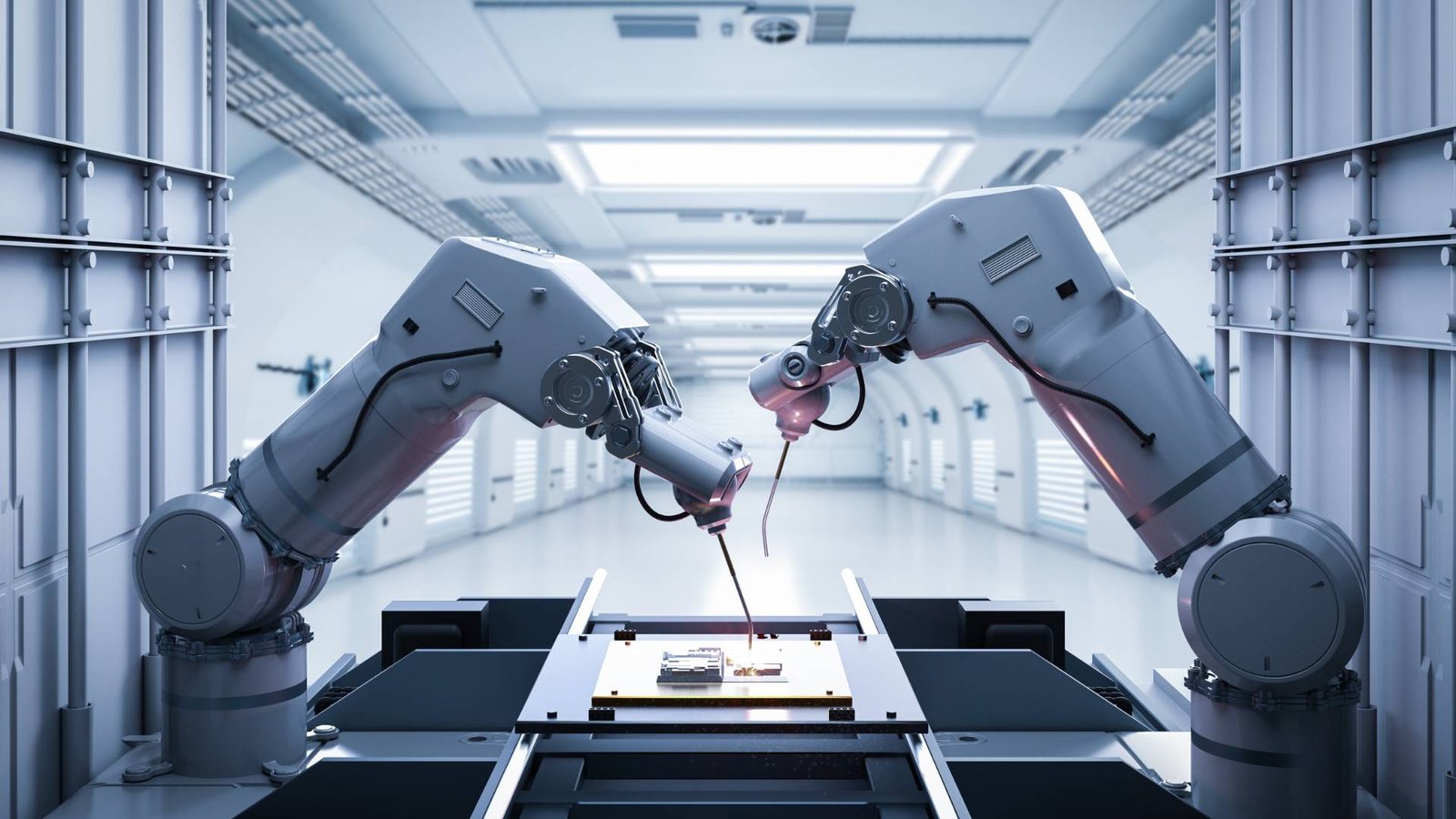
In the realm of automation technology, linear actuators play a crucial role, offering unmatched capabilities in terms of precision and control. They are integral components in a wide range of applications, driving innovation across various sectors. A paramount example of their utility can be found in Linear Actuator systems that serve diverse industrial needs.
Understanding Linear Actuators
Linear actuators are devices that convert energy, usually electrical or hydraulic, into linear motion. This motion is a straight line as opposed to the rotational movement offered by traditional motors. The simplicity and efficiency of linear actuators make them ideal for various automated tasks requiring straight-line motion.
Types of Linear Actuators
There are several types of linear actuators, each catering to specific requirements and environments. The primary types include electric, hydraulic, and pneumatic actuators, each offering unique advantages.
Electric Linear Actuators
Electric linear actuators are perhaps the most versatile. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, providing precise control over movement and speed. These actuators are particularly valuable in precision applications such as robotics and manufacturing where exact positioning is critical.
Hydraulic Linear Actuators
Hydraulic actuators use fluid pressure to achieve movement. They are known for their strength and are ideal for heavy-duty applications where the force is essential. Their robustness makes them suitable for tasks like lifting or pressing where large loads need to be managed with care.
Pneumatic Linear Actuators
Pneumatic actuators operate using compressed air. They offer a cost-effective solution for applications where speed and repetitive motions are required. However, they are less precise than their electric counterparts, which limit their use in precision-demanding environments.
Applications of Linear Actuators
Linear actuators are employed across various industries, from automotive to healthcare. In the automotive industry, they automate processes such as engine control and adjust seating positions. In healthcare, they contribute to the development of advanced prosthetics and hospital beds.
Automation and Manufacturing
In manufacturing, linear actuators are pivotal in automating the assembly lines and enhancing productivity. They are used for positioning components accurately, which improves the quality of end products and optimises the production process.
Robotic Systems
Robotic systems rely heavily on linear actuators for movement and function. From picking and placing items to performing complex surgical operations, actuators form the backbone of modern robotics by ensuring precise and controlled motion.
The Future of Linear Actuator Technology
As industries continue to seek greater automation and efficiency, the evolution of linear actuators is expected to advance rapidly. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning may further enhance actuator capabilities, introducing smarter and more adaptive solutions.
Innovative Material Use
One promising development is the use of lightweight and durable materials to improve actuator efficiency and lifespan. This evolution will cater to the needs for more energy-efficient systems that reduce operational costs while delivering high performance.
Integration with IoT
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology with linear actuators is another exciting frontier. This will enable real-time monitoring and control, leading to more responsive and adaptable automation systems that can quickly adjust to changing conditions and demands.
Conclusion
The advancement of automation through linear actuators represents a significant leap towards enhanced industrial efficiency and productivity. By offering precise, reliable, and powerful solutions, actuators not only streamline operations but also foster innovation in emerging technologies. As industries progress, linear actuators will undoubtedly continue to be pivotal elements in the landscape of technology and automation.